Researchers Develop Handheld 3D Printer To Repair Skeletal Muscle Injuries
A group of biomedical engineers, led by associate professor Dr. Ali Tamayol from the University of Connecticut, has developed a handheld 3D bioprinter that can be potentially used to help repair and regrow lost tissue in muscles.
This compact handheld 3d printer allows surgeons to directly place tissue material on damaged skeletal muscles. The tissue material used with this 3D printer resembles the native tissue. The group behind this invention sees potential in it in helping treat Volumetric Muscle Loss. VML is the loss of skeletal muscle because of trauma, resulting in function loss.
Currently, VML requires reconstructive surgery that involves images of the defect site, generating 3D models and then 3D printing the tissue material, which has proven to be time consuming and challenging. This handheld 3D printer overcomes those challenges by directly printing tissue material even on non flat surfaces, as seen in the image above.
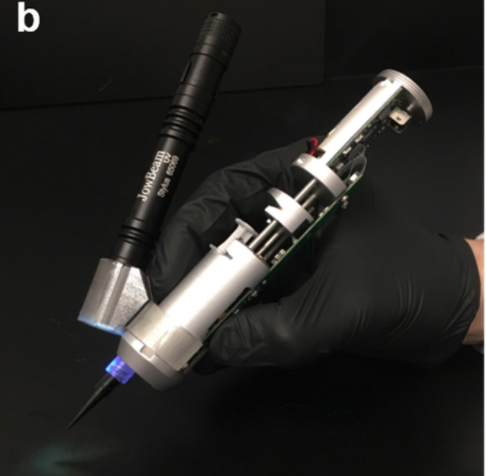
This bioprinter is currently being tested. However, Dr. Tamayol and another co-author have filed for a patent, indicating promising future for this concept. Read the source link to get details on this bioprinter, its mechanism, material used in it, etc.
Source: 3D Printing Industry


Wow, Pretty amazing. I am watching West World Right now, so you know the possibilities of this technology could one day be part of the norm.